The Local Control and Accountability Plan (LCAP)
How Does the LCAP Work?
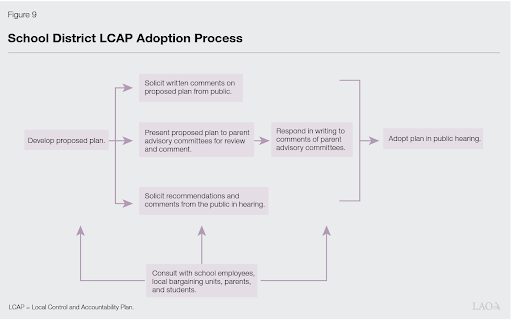
Beginning in 2014, each district, county office of education, and charter school (each LEA) became responsible for preparing a Local Control Accountability Plan (LCAP). The LCAP is a required document under LCFF that describes the overall vision for students, annual goals, and specific actions that will be taken to achieve the LEA’s vision and goals. It is developed and reviewed each year in coordination with the LEA’s annual budget cycle, and LEAs use a template adopted by the State Board of Education (SBE). The graphic below provides a quick overview of the adoption process. v
LCAP Overview
The Local Control and Accountability Plan (LCAP) is a three-year plan adopted by the LEA that describes how they will focus on supporting positive student outcomes that align with the state and local priorities by describing specific goals, actions, services, and expenditures. It is a picture of what the LEA is striving to achieve and how they plan to do so. In their LCAPs, districts are required to develop explicit plans for distributing funding to their most at-promise students.
According to the LCAP template instructions, developing the LCAP serves three distinct and related functions:
- Meaningful engagement of educational partners
- Comprehensive strategic planning
- Accountability and compliance
For the 2023-2024 LCAP year, the components of the LCAP are as follows (it is important to note that LEAs must post these as one document in the following order):
- LCFF Budget Overview for Parents
- Plan Summary
- Engaging Educational Partners
- Goals and Actions
- Increased or Improved Services for Foster Youth, English Learners, and Low-income students
- Action Tables
- Instructions
The LCAP components are described in detail below.
LCFF Budget Overview for Parents
The LCFF Budget Overview for Parents intends to facilitate a better understanding of the funding included in the LCAP. To the greatest extent possible, the LCFF Budget Overview for Parents should use language that is understandable and accessible to parents.
The LCFF Budget Overview for Parents is subject to the same requirements for adoption, review, and approval as the LCAP.
The LCFF Budget Overview for Parents must be attached as a cover to the LCAP. In addition, the document must be included in the review and approval of the LCAP and must be posted on the LEA’s website with the LCAP as a single document.
Plan Summary
The LCAP instructions, outlined by the California Department of Education, describe a well-developed Plan Summary section as one that “provides a meaningful context for the LCAP” and helps all readers understand the LEA’s priorities and goals (CDE, 2024). The Plan Summary intends to provide information about an LEA’s community, give a brief overview of student needs and performance, and highlight elements in the LCAP that the LEA believes are important. To provide a meaningful context for the rest of the LCAP, the content of this section should be clearly and meaningfully related to the content included in the subsequent sections of the LCAP. LEAs are encouraged to view the summary as an opportunity to tell their story in concise and easily understandable terms. Each of the summary sections must be updated each year. The Plan Summary includes:
LEAs briefly describe the LEA, its schools, and its students in grades TK–12, as applicable to the LEA. The LCAP instructions outline that an LEA may wish to describe their “geography, enrollment, or employment, the number and size of specific schools, recent community challenges, and other such information as an LEA wishes to include can enable a reader to more fully understand an LEA’s LCAP” (CDE, 2024).
The reflections within the annual performance section of the LCAP should include both local data and the annual performance on the CA School Dashboard, addressing both the successes and challenges that the LEA has experienced and identified during the process of developing the LCAP. LEAs are required to respond and include the following information (this information should remain in the response for the three-year cycle of the LCAP). Please note that these are directly called out within the LCAP template instructions (CDE, 2024).
- “Any school within the LEA that received the lowest performance level on one or more state indicators on the 2023 Dashboard;”
- “Any student group within the LEA that received the lowest performance level on one or more state indicators on the 2023 Dashboard; and/or”
- “Any student group within a school within the LEA that received the lowest performance level on one or more state indicators on the 2023 Dashboard.”
This portion of the LCAP Plan Summary must include a description of the work in progress through Technical Assistance. The most common form of Technical Assistance is the Differentiated Assistance (DA) process, however, additional Technical Assistance requested from the County Office of Education should also be included. The LCAP template requires that the LEA “Annually identify the reason(s) the LEA is eligible for or has requested technical assistance consistent with EC sections 47607.3, 52071, 52071.5, 52072, or 52072.5” (CDE, 2024). If this does not apply to the LEA, they may enter “NA.”
Any school(s) within the LEA that has been identified for comprehensive support and improvement (CSI) under the federal Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) must complete this section and include the schools identified, the support for those identified schools, and how the plan for support for these schools is being monitored and evaluated.
Engaging Educational Partners
Meaningful engagement of all educational partners is critical to developing an effective LCAP and to the overall budget process. The Engaging Educational Partners section of the LCAP describes the consultation process the LEA had with various educational partner groups, which could include the parent advisory committee, the English learner parent advisory committee, teachers, principals and administrators, other school personnel, special education local plan area (SELPA) administrator(s), local collective bargaining units, parents, students, and any other community-based organizations identified by the LEA.
The second portion of this module has been dedicated to the topic of engaging educational partners due to the significant nature of this work. For more information now, you can jump down to the Engaging Educational Partners section of the module.
Goals and Actions
Meaningful engagement of all educational partners is critical to developing an effective LCAP and to the overall budget process. The Engaging Educational Partners section of the LCAP describes the consultation process the LEA had with various educational partner groups, which could include the parent advisory committee, the English learner parent advisory committee, teachers, principals and administrators, other school personnel, special education local plan area (SELPA) administrator(s), local collective bargaining units, parents, students, and any other community-based organizations identified by the LEA.
The second portion of this module has been dedicated to the topic of engaging educational partners due to the significant nature of this work. For more information now, you can jump down to the Engaging Educational Partners section of the module.
To support the prioritization of goals, the LCAP template provides LEAs the ability to develop several different types of goals in alignment with addressing the required LCFF priorities:
- Focus Goal: A focus goal is concentrated in scope and focuses on explicit metrics to measure progress. A focus goal statement will have a firm timeline and make clear how the goal is to be accomplished. LEAs receiving Equity Multiplier funds are required to include a focused goal for each school that has generated the Equity Multiplier funds.
- Broad Goal: A broad goal is less concentrated than a focused goal in its scope and may have multiple metrics that can be used to measure progress.
- Maintenance of Progress Goal: A maintenance of progress goal includes actions that “maintain the progress made in the LCFF Priorities not addressed by the other goals of the LCAP” (CDE, 2024).
The LEA is required to outline the specific metric(s) being used to measure progress on the expected outcomes. There are required metrics for both LEA-wide actions and Equity Multiplier goals.
This portion of the Goals and Actions section includes a description of how the specific goal was implemented in the prior year. Several prompts provide the reader with more information on how the goal was implemented, any differences between the planned and actual expenditures/improved services, as well as a review of the effectiveness of the progress of the goal thus far.
Following the goals and goal analysis, the template includes an action table with a short description of the action and the total amount of expenditures aligned with the action, as well as if the action contributes towards the increasing or improving services requirement. There are required actions for the following scenarios/LEAs:
- LEAs with 30 or more students who are English learners and/or 15 or more students who are long-term English learners
- LEAs engaging in technical assistance (pursuant to EC sections 47607.3, 52071, 52071.5, 52072, or 52072.5) are required to include actions tied to the work that has been implemented in conjunction with the technical assistance
- LEAs that have been identified with a Red Dashboard indicator(s) for either a school within their LEA, a student group in the LEA, and/or a student group at any school within the LEA
Increased or Improved Services for Foster Youth, English Learners, and Low-Income Students for LCAP Year
This component of the LCAP is intended to provide readers with a description of how the LEA will increase or improve services to their unduplicated student groups as compared to the services provided to all students. Additionally, it outlines how the actions (both LEA-wide and schoolwide) identified to do so will meet the statutory requirements. The LCAP template states that “To improve services means to grow services in quality and to increase services means to grow services in quantity” and actions identified as such are also indicated in the prior action tables (CDE, 2024). LEAs are required to describe the LEA-wide and schoolwide actions that are being implemented to increase or improve services to these students within a table in this component. Actions being implemented solely to one or more of the unduplicated student groups are called out within a Limited Actions section of the template, followed by a description of the LEA’s plan for the use of additional concentration grant add-on funding.
Instructions
The final pages of the LCAP template provide the writer with thorough descriptions of each prompt and component of the template.
Additional Requirements
SB997
This bill requires, beginning July 1, 2024, the governing board of a school district serving middle school or high school pupils and a county superintendent of schools to either include at least 2 pupils as full members of the parent advisory committee to serve for a renewable term of one full school year, or to establish a student advisory committee as specified. (Education Code Section 52063)
Before adopting the LCAP, LEAs, and COEs must share the LCAP with the following:
- Parent Advisory Committee (PAC)
- English Learner Parent Advisory Committee (if applicable)
The statute specifically requires the governing board of the LEA to establish the PAC, so if the governing board is going to pass that responsibility off to the LEA, it needs to communicate that information. PAC meetings are public meetings that any public member may attend and address items on the agenda, consistent with the open meeting requirements in EC Section 35147.